Understanding Lead-Acid Car Batteries: Structure, Functionality, and Maintenance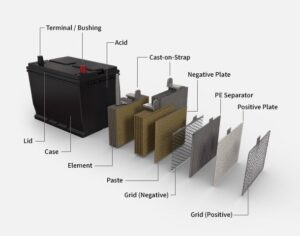 Lead-acid batteries have been a cornerstone of automotive power since their invention in 1859 by French physicist Gaston Planté. Despite advancements in battery technology, they remain the predominant choice for vehicles worldwide. This article delves into the structure, functionality, advantages, and environmental considerations of lead-acid car batteries.
Lead-acid batteries have been a cornerstone of automotive power since their invention in 1859 by French physicist Gaston Planté. Despite advancements in battery technology, they remain the predominant choice for vehicles worldwide. This article delves into the structure, functionality, advantages, and environmental considerations of lead-acid car batteries.
Structure and Functionality
A typical lead-acid battery comprises six cells, each producing approximately 2.1 volts, collectively delivering around 12.6 volts when fully charged. Each cell contains positive plates coated with lead dioxide (PbO₂) and negative plates made of sponge lead (Pb), immersed in an electrolyte solution of sulfuric acid (H₂SO₄) and water. During discharge, a chemical reaction occurs where both plates convert to lead sulfate (PbSO₄), releasing electrical energy. Recharging reverses this process, restoring the original materials and readying the battery for another cycle.
Advantages of Lead-Acid Batteries
Lead-acid batteries offer several benefits that have sustained their use in automotive applications:
Cost-Effectiveness: They are less expensive to produce compared to newer technologies, making them economically viable for mass-market vehicles.
Reliability: Proven performance over decades has established their dependability in various conditions.
High Surge Currents: Capable of delivering the substantial current required to start vehicle engines.
Recyclability: Lead-acid batteries are highly recyclable, with over 95% of their components being reusable, reducing environmental impact.
Environmental Considerations
While lead-acid batteries are recyclable, improper disposal and recycling practices can lead to environmental contamination. This highlights the necessity for stringent regulations and responsible recycling methods to mitigate environmental hazards.
Maintenance Tips
To maximize the lifespan and performance of lead-acid car batteries:
Regular Charging: Avoid deep discharges; recharge the battery promptly after use.
Cleanliness: Keep terminals and casing free from dirt and corrosion.
Secure Mounting: Ensure the battery is properly secured to prevent vibrations that can cause damage.
Routine Inspections: Regularly check for signs of wear, such as cracks or leaks, and replace the battery as needed.
Lead-acid batteries continue to be integral to automotive applications due to their cost-effectiveness, reliability, and recyclability. Proper maintenance and responsible recycling are essential to sustain their benefits while minimizing environmental impacts.